This SS-General if someone tears up opinions, was he a war criminal or a clever organizer with a good side? If you read post-war literature, the veterans seem to have praised him highly. They gave him the epithet “Papa” early on.
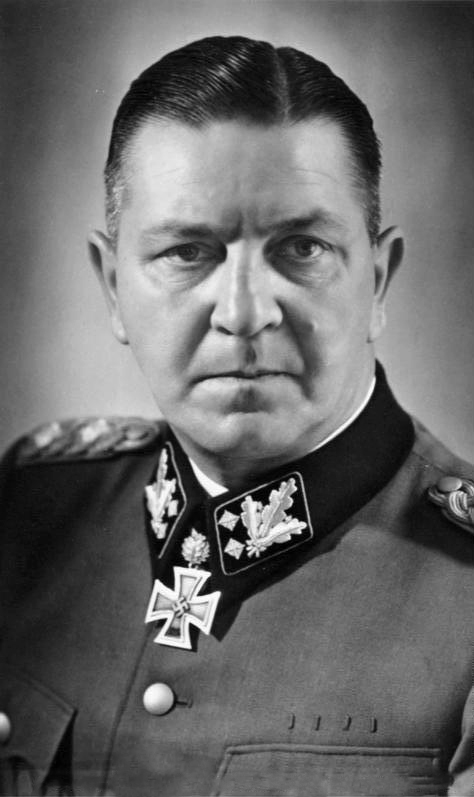

the fact is that he was the one who organized how a German concentration camp was built, why I write in German is that concentration camps were not a German invention, but created by the English during the war in South Africa, the so-called Boer war.
Eicke’s organization meant that a concentration camp had 6 departments, as well as a guard unit in the form of an SS-Totenkopfverbände. Ab I. In was the commandant’s and its adjutant’s department. Abt II, the camp was the “Gestapo”, this was independent of the commandant and other staff. Abt III. Where the camp itself in German was called “Schutzhaftlager” this department had its own commandant who had the title “Schutzhaftlagerführer”. Department IV was the administration and had everything to do with the camp’s economy. Dept. V was the domain of the doctors. They were often also responsible for the troops that were around the camp. Department VI was the political unit responsible for ensuring that the troops at the camp received the right training in National Socialism. The unit that guarded the camp was first called “Wachsturmbann” to later get the title SS-Totenkopfverbände, there were four such units 1, 2, 3 and 4 these four were responsible for guarding the camp. Before the war, the soldiers in the SS-TV units were on a rolling schedule, one week in the towers or around the fence and three weeks of military exercises. During a conversation with a veteran who admitted that he had served in KL Buchenwald between 1938-1940, when asked what it was like to guard the camp, the simple answer was “it was really boring”.
But enough about the camps, after Eicke created this model, in 1936 he was appointed supreme director of the SS-TV and Concentration Camps, his new position meant that he settled just south of KL Sachsenhausen (the villa remains and is today a youth hostel). They also built a large complex in the shape of a T, hence the name “T-Gebäude”, this building also remains, it contains a small museum otherwise the Finance Department of the state of Brandenburg takes possession of the rest of the building.
At the end of the war in 1939, parts of the SS-TV participated in the battles in Poland, mainly 2.SS-TV Brandenburg, were involved and they are said to have committed one of the first war crimes of the war. For Eicke this meant little and he praised all his soldiers. Eicke was a leader who in duty he demanded blind obedience, while in his spare time he was one of his soldiers and there are plenty of pictures of Eicke sitting in the middle of his unit smoking his pipe and saying hello to all his soldiers, which even they could do under the relaxed forms. But pity the one who had the nerve to say hello to his general in the service. Then they quickly risked having to put on the striped clothes and see themselves as prisoners in one of the camps.
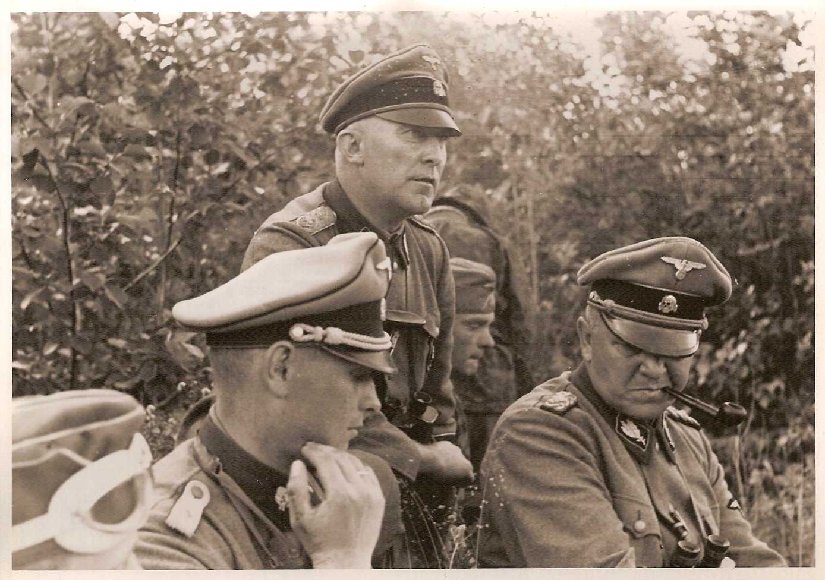

I have documents where soldiers had to leave their post at 1.SS-TV Oberbayern (Dachau) to see themselves transported under guard to KL Buchenwald to see themselves there as prisoners.
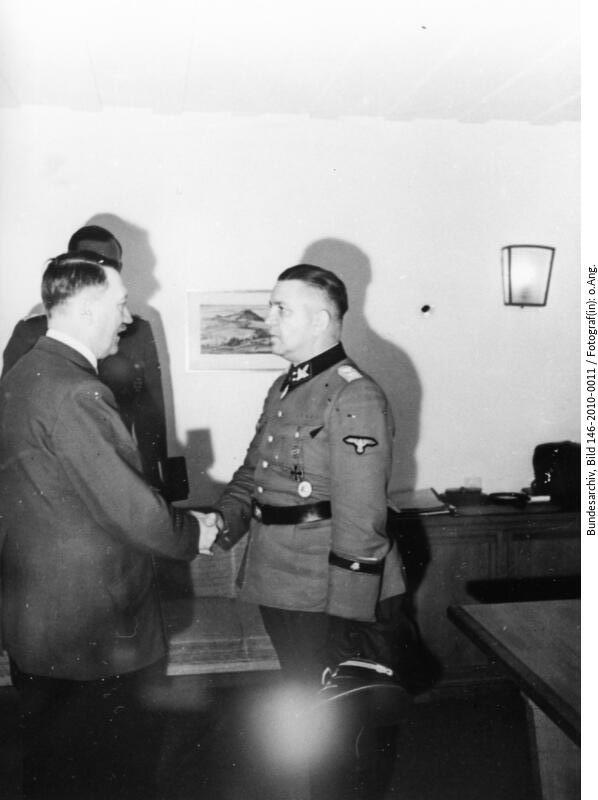
Eicke’s leadership was not looked upon kindly by other senior leaders within the SS and the party, he often got into arguments with his superiors and not infrequently RFSS Himmler had to step in, either to reprimand Eicke, but also sometimes to give him the right and with a try to get Eicke to accept that certain things must work in certain ways. This was something of a common thread in Eicke’s life. But still he was admired by his soldiers, both privates and officers.
in October 1939, the SS-Totenkopf Division was formed in Dachau, which had been emptied of prisoners only to accommodate all the new recruits and soldiers. The prisoners were mainly transferred to KL Mauthausen. They began training hard for upcoming battles, and the SS-Totenkopf Division received its baptism of fire in the Battle of France. There, the SS-Totenkopf committed a war crime that echoed far up among the generals of the regular army. What happened was that Fritz Knöchlein executed a unit from the English army at La Paradis, Eicke protected his soldiers and thought it was not so remarkable. But after pressure from both the RFSS and others, Fritz Knöchlein was withdrawn from the front. One might think that this Knöchlein would fall out of favor, but no he was later decorated with the Knight’s Cross and reached the rank of lieutenant colonel in the Waffen-SS (SS-Obersturmbannführer).
After the Battle of France, the SS-Totenkopf Division had a relatively quiet period, being used as garrison troops in France while training under the watchful eye of Eicke.

When the Battle of Barbarossa began, the SS-Totenkopf Division was part of the attack and they advanced through Poland (the Russian occupied territories) Lithuania, parts of Latvia towards the great Lake Ilmensee, a lake that would become very associated with the SS-Totenkopf Division and Theodor Eicke.
Even times Eicke was transferred to Hitler’s headquarters, he constantly requested transfers to return to his soldiers who were enclosed in what came to be known as the “Demjansk Pocket”. After eternal nagging from Eicke, who kept sending telegrams to SS-Gruf Simon and others. so he finally got to return to his beloved Division. he regained the lead and immediately launched a mass counterattack against the Russians. Under Eicke’s leadership, many soldiers and officers received high honors in the battles that followed. Fritz Christen who was part of the SS-Totenkopf-Pz.Jg.Abt was the first private to be awarded the Knight’s Cross. But countless others received this high distinction.
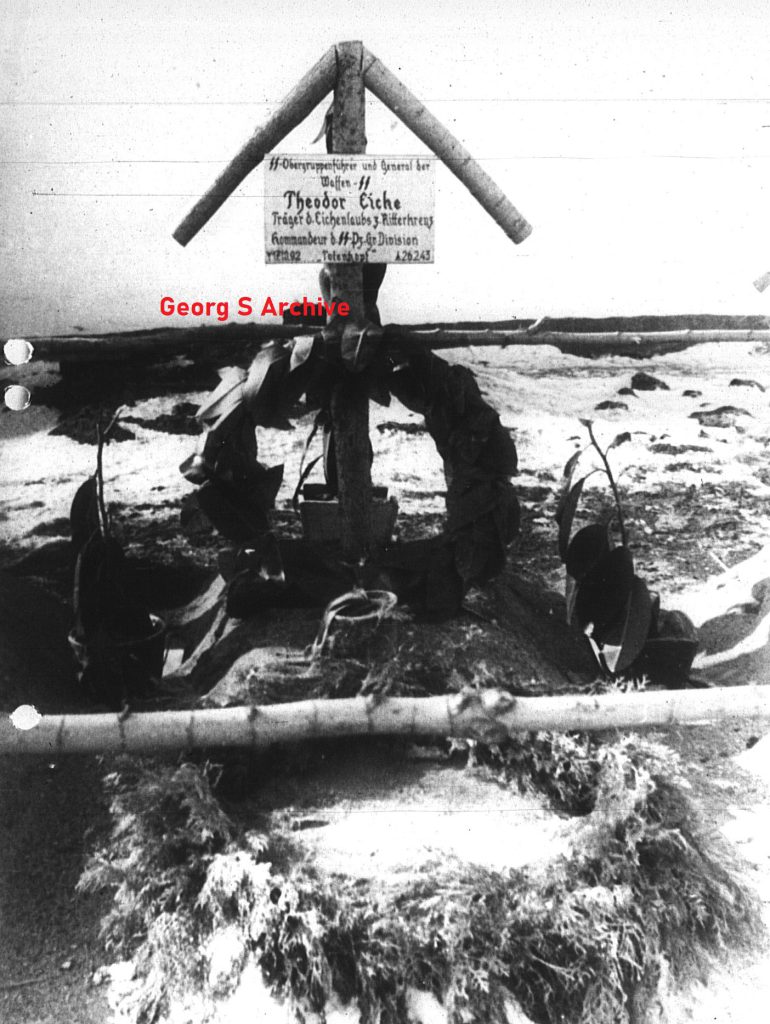
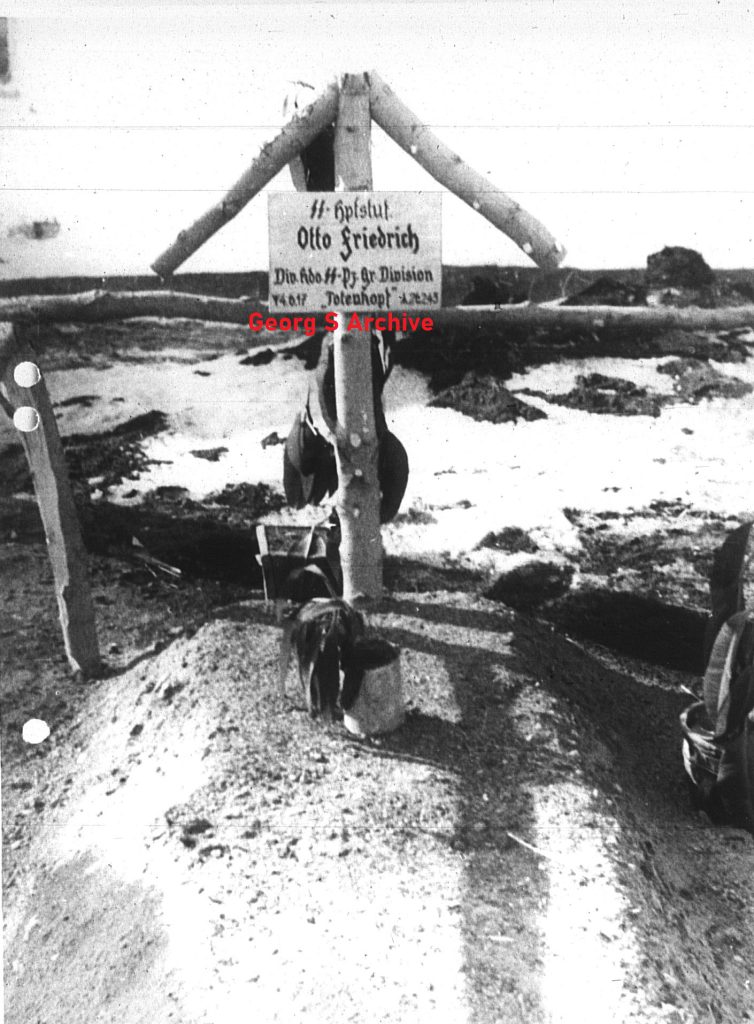
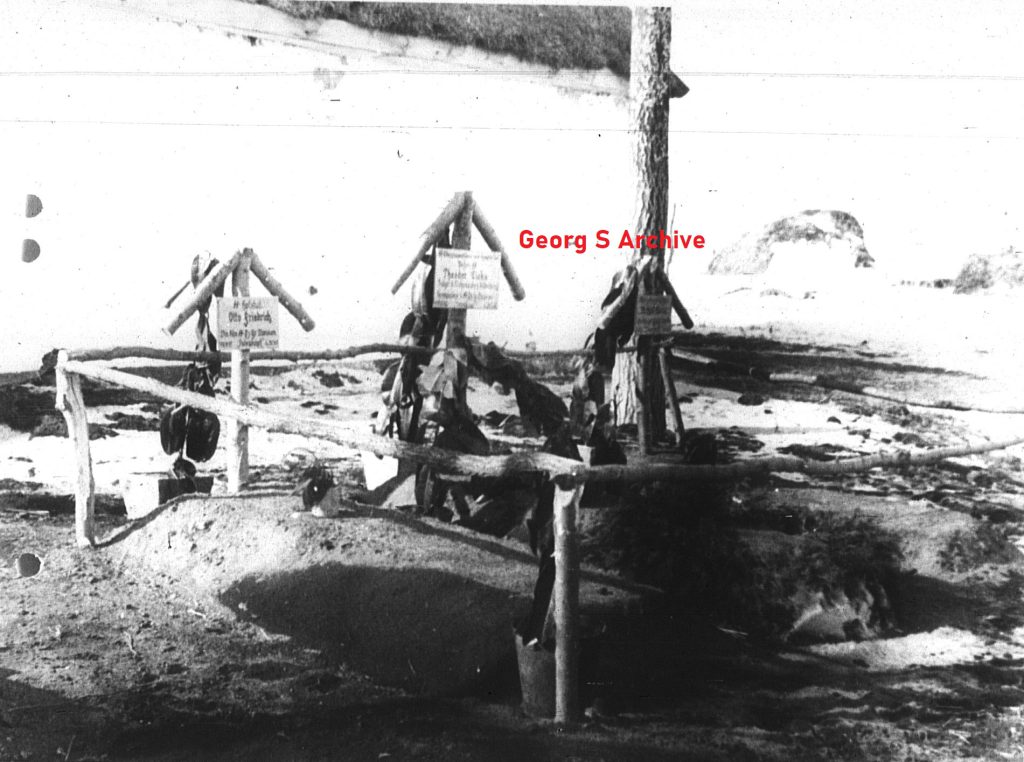
Demjansk would also mean that the story of Theodor Eicke would end, during a reconnaissance flight with his Fiesler Storch, his aircraft was shot down by the Russians and all on board died. This happened on February 26, 1943. The soldiers of the SS-Totenkopf Division did not believe it was true and a rescue operation was put in place, if not to recover the bodies. Eicke hated the Russians and letting him fall into the hands of the Russians was completely out of the question for the soldiers of the “SS-Totenkopf”
Theodor Eicke left behind a wife and daughter, his son had died a year earlier as a lieutenant in a Panzer unit. his daughter was also married to SS-Ostubaf Karl Leiner. Eicke’s wife was given permission to continue living in their villa south of KL Sachsenhausen.
If Theodor Eicke would have survived the war, he sure would have been prosecuted and condemed for warcrimes.
The first grave for Theodor Eicke and the two other men who died in the same plane after they was shot down,





//Georg